The debate on banning social media for minors in the UK and Australia
November 25, 2024

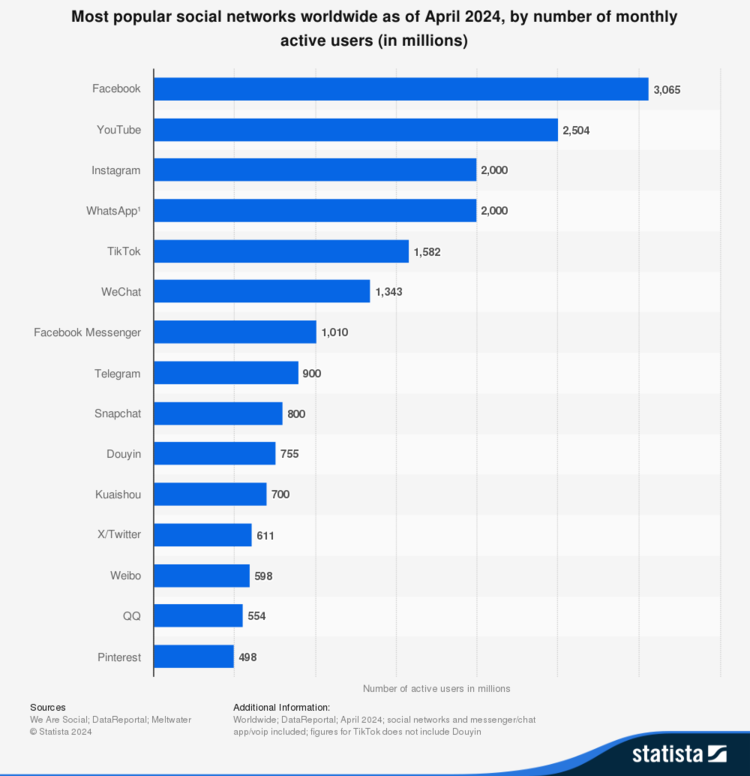
Social media has become an essential part of modern life, with billions of people connecting daily through these platforms. According to recent statistics, Facebook leads as the most popular social network, with 3.065 billion monthly active users in April 2024. It’s followed by YouTube, with 2.504 billion, and Instagram and WhatsApp, both with 2 billion active users. These figures not only reflect the global influence of these platforms but also their relevance across all age groups. However, the growing concern about the impact social media can have on minors has sparked significant debate worldwide.
With governments in the UK and Australia considering banning access to social media platforms for minors under 16, an important question arises: how would digital consumption change if these restrictions were implemented?
Social media and minors: a delicate balance
The popularity of platforms like TikTok (1.582 billion users) and Snapchat (800 million) largely comes from their ability to attract a young audience. These platforms offer dynamic, personalized content designed to capture users’ attention. However, it is these very features that raise concerns about digital addiction, exposure to inappropriate content, and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
Government concerns
Both the UK and Australia argue that these social networks can be harmful to young people due to:
- Increased addiction: Platforms are designed to keep users’ attention, promoting compulsive usage patterns.
- Exposure to harmful content: From cyberbullying to inappropriate material, minors may be at risk of encountering damaging situations.
- Impact on mental health: Numerous studies have linked excessive social media use to self-esteem issues, anxiety, and depression, especially among teens.
These concerns have led to the consideration of bans that could change the way new generations interact in the digital space. However, not everyone agrees with this approach.
Criticism of bans: freedom and alternatives
While some defend restrictions as a protective measure, other tech leaders, such as Elon Musk, propose an alternative focused on education and awareness. According to Musk, limiting access to social media won’t solve the underlying issue, as minors could migrate to less regulated platforms or find ways to bypass restrictions.
Elon Musk stated: “Minors need protection, but we shouldn’t limit them entirely. The goal should be to educate, empower, and provide them with tools to navigate a digital world that is becoming increasingly present.”
In this regard, critics argue that:
- Social media can be a valuable educational and socialization tool for minors if used correctly.
- Banning access doesn’t address the root problem, which is the addictive design of the platforms and lack of proper supervision.
- Bans could push teens toward unregulated apps, where they would be even more exposed to risks.
The impact on social platforms: how would consumption change?
If restrictions were implemented banning minors from accessing platforms like TikTok, Snapchat, or Instagram, global usage statistics would likely undergo significant changes. For example:
- TikTok could see a drop in its user base, as much of its audience is made up of teens.
- Snapchat, which heavily relies on young users, could face challenges in maintaining its relevance.
- Platforms like Facebook or YouTube, which have broader and more diverse audiences, might be less affected but could still adapt to meet new regulations.
A middle ground: education as a solution
Instead of imposing strict bans, many experts suggest a middle ground that combines:
- Digital education: Teaching minors about the risks of social media and promoting responsible use. This could include workshops in schools, awareness campaigns, and educational programs led by the platforms themselves.
- Parental controls: Offering tools that allow parents to monitor and limit their children’s social media use. This would include time limits, content filtering, and stricter privacy settings.
- Platform responsibility: The companies behind these social networks must take an active role in protecting their younger users. This could involve:
- Improving algorithms to avoid promoting addictive content.
- Implementing more effective content filters.
- Creating versions tailored to minors, with age-appropriate features.
Towards conscious digital consumption
The debate over the relationship between minors and social media does not have a simple solution. On one hand, bans may offer a layer of protection but also limit young people’s ability to learn and connect in a digital world. On the other hand, education and awareness may be more sustainable strategies, though they require a long-term commitment from governments, parents, and tech companies.
Incorporating these measures could lead to a positive shift in how new generations consume social media, balancing its educational and social potential with the protection necessary for their well-being. Ultimately, the responsibility is shared: as a society, we must equip young people with the tools they need to navigate safely and consciously in an increasingly digital world.




